Description:
Following a firmware downgrade, some parts of the configuration may not have existed in the earlier LCOS version. As a result, changes to the configuration that were performed in LANconfig cannot be written back to the device. An SNMP error is output instead.
This article describes how to use the command line to check which part of the configuration is causing the SNMP error, and how to fix it.
Requirement:
- SSH client, e.g. PuTTY
- LANtools as of version 9.00 (download latest version)
Procedure:
1) Identify the command-line path of the bad parameter:
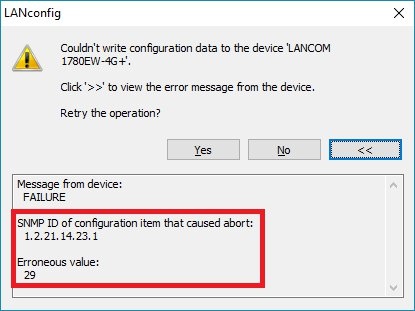
1.1) Make a note of the SNMP ID shown in the error message along with the Erroneous value.
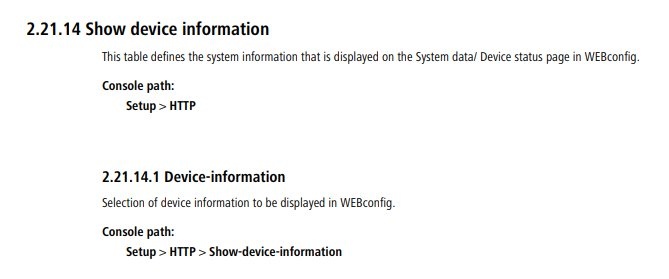
1.2) Download the English Menu Reference Guide to check which command-line path is behind the SNMP ID.
You will need the English version of the Menu Reference Guide because the language on the command line is English.
1.3) In the Menu Reference Guide, look for the SNMP ID while omitting the first and last digits. In this example, this would be 2.21.14.23.1.
Although the Menu Reference Guide does not contain the SNMP ID 21.2.14.23, it does contain the SNMP ID 2.21.14, which corresponds with the command-line path Setup/HTTP/Show-device-information.
2) Restoring the default values in the relevant path:
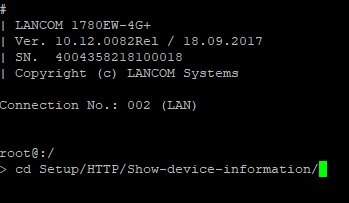
2.1) Use an SSH client with root privileges to connect to the device and issue the command cd followed by the command-line path identified in step 1.3:
cd Setup/HTTP/Show-device-information
Alternatively, you can enter the SNMP ID. In this case cd 2/21/14.
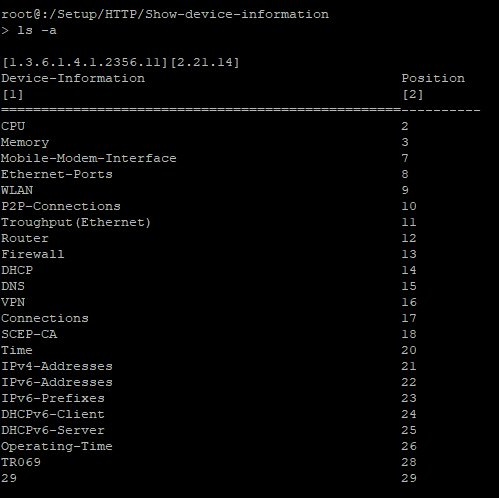
2.2) Enter the CLI command ls -a.
The bottom row shows the faulty parameter 29.
Additionally entering the parameter -a will display the SNMP path.
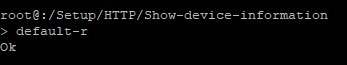
2.3) Execute the command default -r to reset this table and all of its child tables (-r stands for recursive) to reset them to their default values.
Make sure you are in the correct table. Executing this command in the root directory will delete the entire router configuration and reset the default values (this applies to all setup tables)!
If manual configuration changes have been made to a table or any of its child tables, then do not reset that table to its default values by using the command default -r. In this case, follow the instructions in step 4.
3) A number of tables contain incorrect parameters:
Potentially, numerous tables can contain incorrect parameters. Resetting them manually would require a considerable amount of effort. In this case, it makes sense to create a script backup of the device, and then to reset the device and restore the script backup. However, this is only possible if you have on-site access to the device.
We recommend that you perform this step each time after you manually corrected 2 – 3 tables, as there is no way of checking the number of erroneous parameters in advance.
If a script backup is uploaded to a device, the only parameters to be accepted are those supported by both the device and the LCOS version.
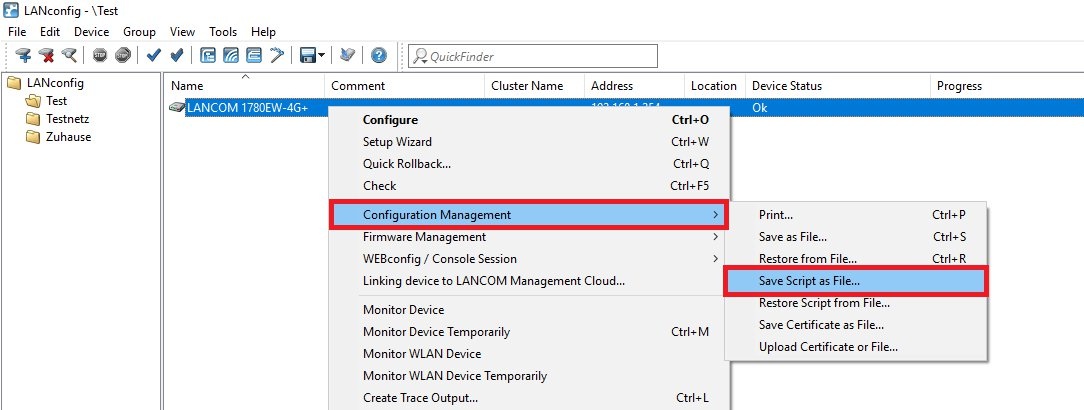
3.1.1) Open LANconfig, right-click on the affected device and select the context menu Configuration Management → Save Script as File.
3.1.2) Reset the device to its factory settings.
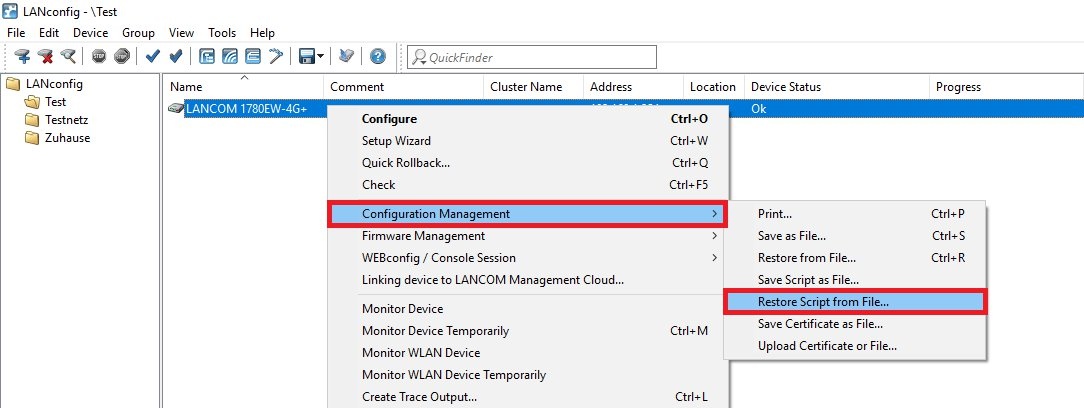
3.1.3) In LANconfig, right-click on the affected device and select the context menu Configuration Management → Restore Script from File.
4) Special case: A manually configured table contains a bad parameter:
If the affected table contains configuration changes made by you (e.g. Setup/WLAN), do not execute the command default -r, otherwise your changes will be lost and reset. Instead, you should only change or delete the incorrect parameter.
4.1) A manually configured table contains a superfluous parameter:
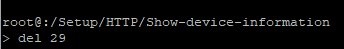
4.1.1) In the command-line path, delete the affected parameter (see step 2.1) with the command del.
4.2) In a manually configured table, an existing parameter is assigned a bad value:
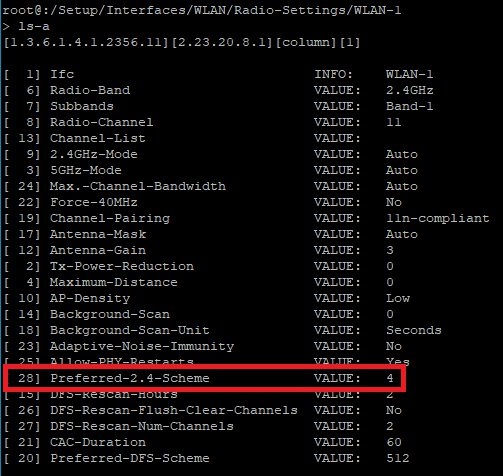
The SNMP ID 1.2.23.20.8.1.28 refers to the command-line path Setup/Interfaces/WLAN/Radio-Settings/. This contains the incorrect value 4.
For better legibility, we changed to the interface WLAN-1 .
4.2.1) Check the Menu Reference Guide to find the default value for this SNMP ID.
The Menu Reference Guide does not specifically mention the 1 for the interface WLAN-1 . Otherwise this entry would have had to be created twice, because some access points come with two WLAN modules.
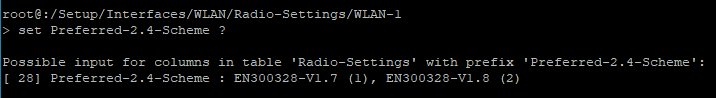
4.2.2) Enter the command set followed by the identifier of the erroneous parameter along with a ?, and copy the default value.
set Preferred-2.4-Scheme ?
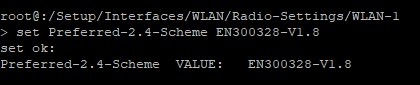
4.2.3) Enter the command set followed by the identifier of the erroneous parameter and the copied default value (see step 4.2.2).
set Preferred-2.4-Scheme EN300328-V1.88
You can also use the SNMP ID instead of the identifier of the erroneous parameter . The commands would then be as follows:
set 28 ?
set 28 2