Description:This document describes the options for error analysis for VoIP configurations. Procedures:1) Check whether the SIP lines are registered with the provider:1.1) Use the command ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/Line at the command line to output the status list of the configured SIP lines.The most interesting columns here are Reg-status, Reg-state and Line-status. In the interests of clarity, the following figure shows a Line table in WEBconfig.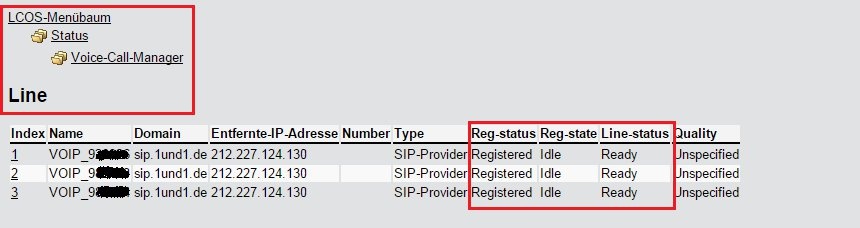 2) Check whether SIP, analog and/or ISDN users are registered: 2) Check whether SIP, analog and/or ISDN users are registered:2.1) Use the command ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/User at the command line to output the status list of the configured SIP, analog and ISDN users.In the interests of clarity, the following figure shows a User table in WEBconfig.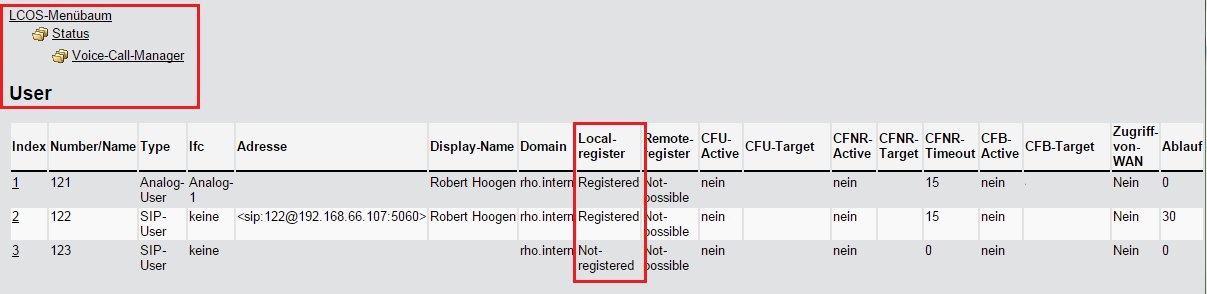 3) Check that calls are being routed to the correct lines: 3) Check that calls are being routed to the correct lines:3.1) Use the command ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/Calls at the command line to output the status list of all of the calls made.The most interesting columns here are the From_Line and the Dest-Line. Here you can see which SIP line was used to route which internal user line (SIP, ANALOG or ISDN).In the interests of clarity, the following figure shows a Call table in WEBconfig.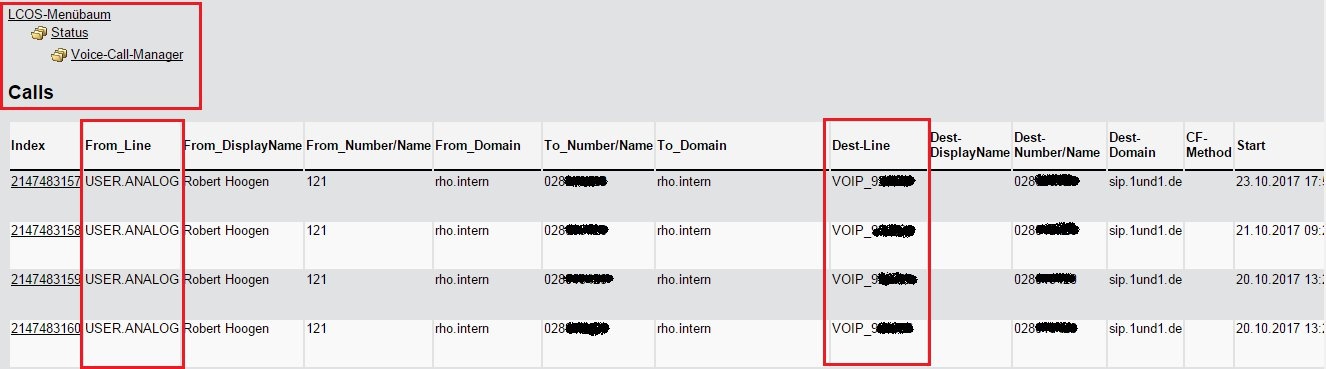 4) Perform traces for troubleshooting and analysis: 4) Perform traces for troubleshooting and analysis:You can capture the following traces with the CLI command tr # <argument> to help with troubleshooting: 4.1) Problems when making a call using the SIP-ALG:- tr # error
- tr # status
- tr # firewall
- tr # sip-alg
- tr # sip-alg-packet
- tr # ip-router
You can also output the following tables:- ls /Status/IP-Router/Connection-List
- ls /Status/IP-Router/Establish-Table
- ls /Status/Sip-Alg/Registrations
- ls /Status/Sip-Alg/Calls
4.2) VoIP problems with an ISDN client:- tr # Callmanager
- tr # D-channel-dump
- tr # Q.931
- tr # status
- tr # error
- tr # sip-packet
- tr # PSTN-MNGMT
You can also output the following tables:- ls /Status/Call-Information
- ls /Status/Connection
- ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/Lines
- ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/Calls
- ls /Status/IP-Router/Connection-List
- ls /Status/ISDN/Line/S0
- ls /Status/ISDN/Framing/PCM-SYNC-SOURCE
- ls /Status/ISDN/Framing/S0
- ls /Status/ISDN/PCM-Switch/PCM-Connection
- ls /Status/ISDN/Signaling/Layer-2/LAPD
- ls /Status/ISDN/Signaling/Management/D-Info
- ls /Status/ISDN/Signaling/Management/Error-Statistic
- ls /Status/Info-Connection
- ls /Status/Voice-Call-Manager/User
4.3) VoIP problems with an analog client:- tr # Callmanager
- tr # D-channel-dump
- tr # status
- tr # error
- tr # B-ANALOG
- tr # DAA
- tr # sip-packet
- tr # SLIC
- tr # Q.931
4.4) Problems when making a call (e.g. call establishment or disconnected calls):- tr # Callmanager
- tr # D-channel-dump
- tr # MEDIA
- tr # MEDIA-CODECS
- tr # MEDIA-PCM
- tr # MEDIA-RT
- tr # Q.931
- tr # sip-packet
If the captured traces are no help with troubleshooting, please send them along with a description of the fault for assessment by LANCOM support. In the case of VoIP, you should always record Wireshark (LCOSCAP) traces from the sending and receiving interfaces.
|
|