Description:
In certain situations, it can be necessary to enable special functions, e.g. to allow connections to the SIP provider or to make sure that the correct telephone number is displayed.
This article describes functions for optimizing VoIP.
(Re)registration and registration interval:
1) (Re)registration:
(Re)registration controls whether registration with the SIP provider takes place. Some lines do not require registration.
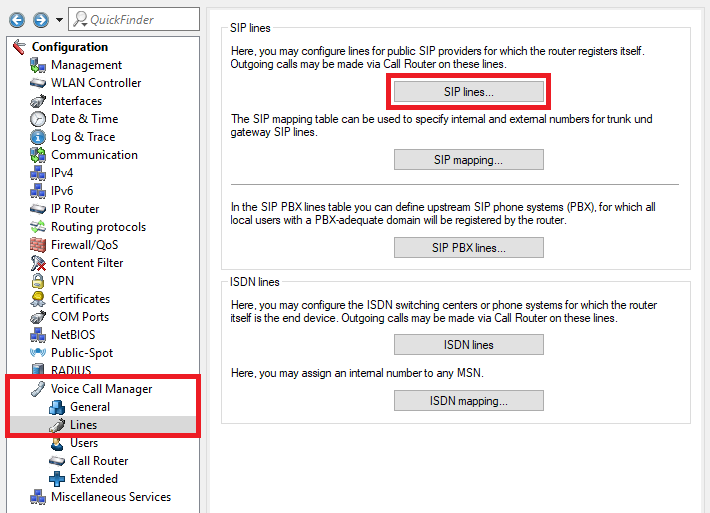
1.1) Open the configuration for the router in LANconfig and navigate to the menu item Voice Call Manager -> Lines -> SIP lines.
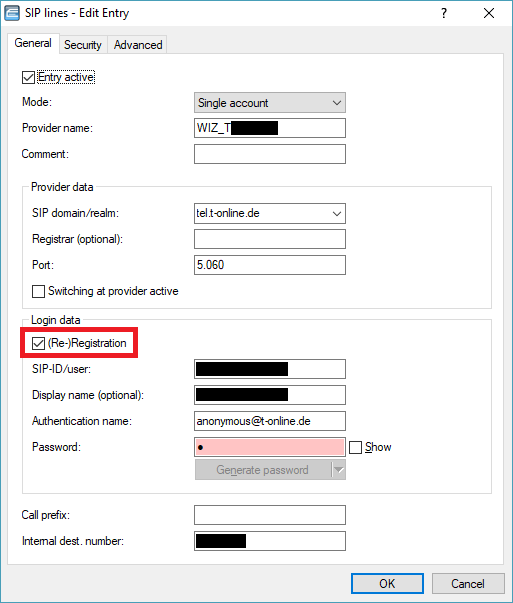
1.2) Edit the desired SIP line and enable or disable (Re-)Registration as needed.
Important:
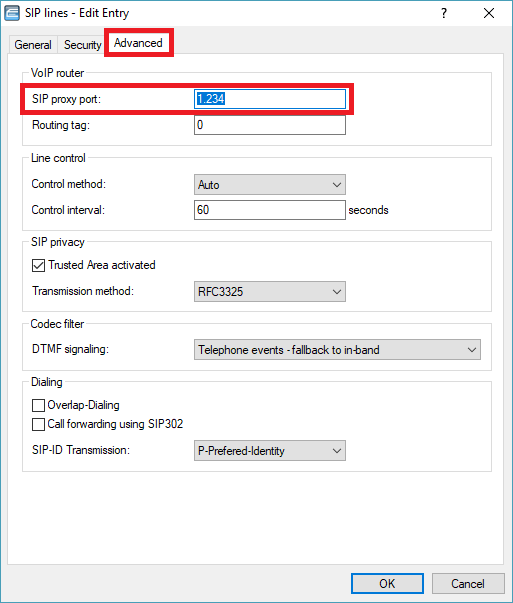
If (Re-)Registration is disabled, the SIP proxy port assigned by the provider must be specified for the SIP line on the Advanced tab.
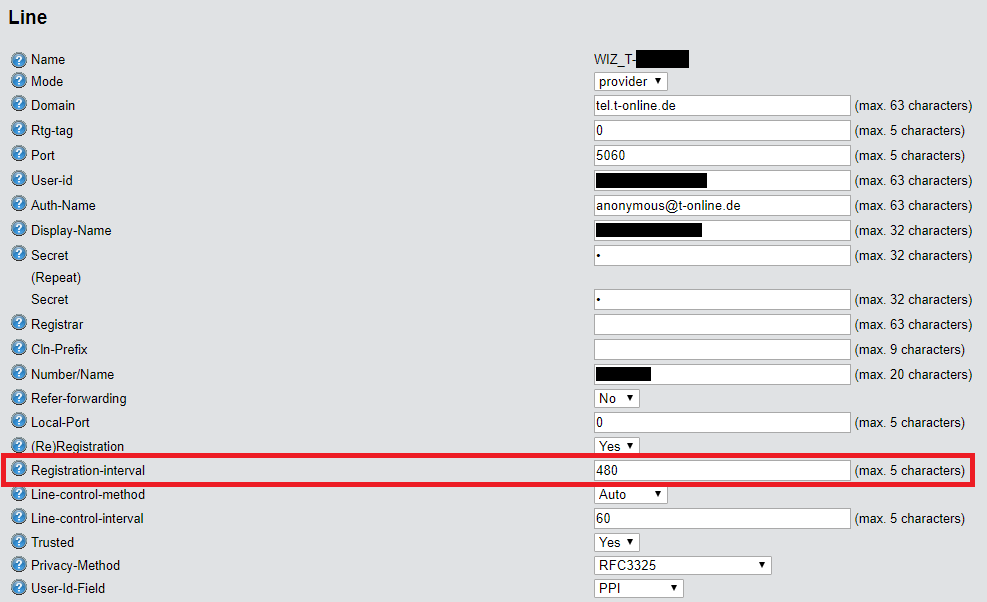
2) Registration interval:
The Registration interval is the interval proposed to the provider by the Voice Call Manager for the registration. By default, the interval is 480 seconds. The Registration interval can only be changed in WEBconfig or via the command line.
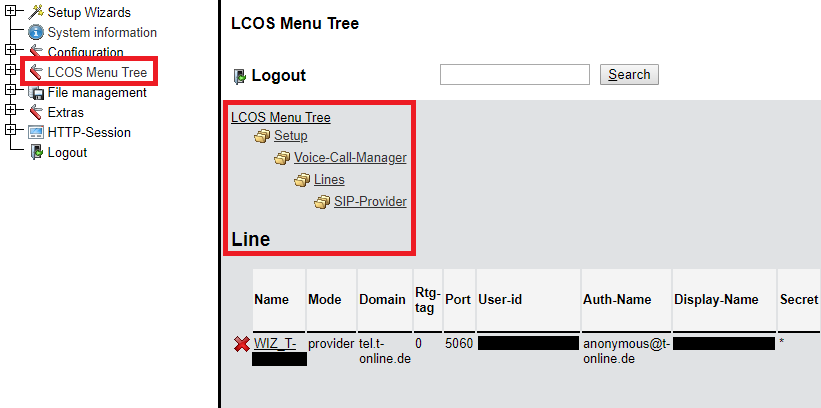
2.1) Use any web browser to connect to the web interface of the router and navigate to the menu LCOS Menu Tree -> Setup -> Voice-Call-Manager -> Lines -> SIP-Provider -> Line -> <Name of the SIP line>.
Info:
The command-line path is Setup/Voice-Call-Manager/Lines/SIP-Provider/Line/<Name of the SIP Line>.
2.2) Change the Registration interval according to your provider’s specifications.
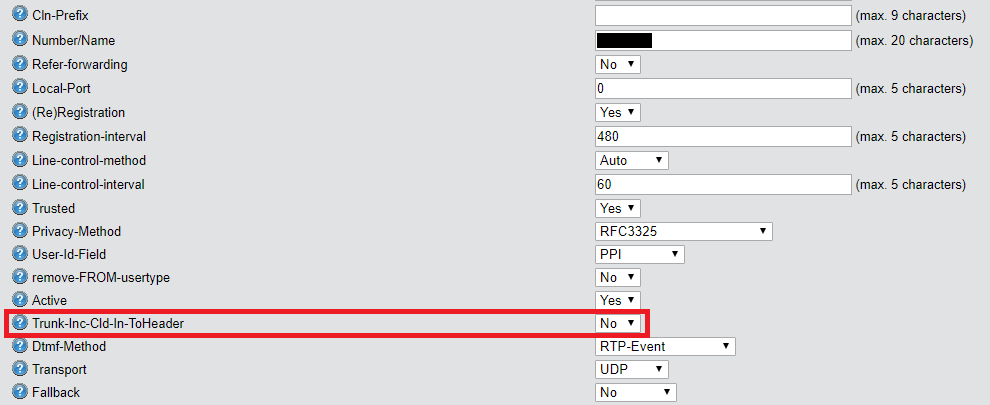
Trunk-Inc-Cld-In-ToHeader:
The function Trunk-Inc-Cld-In-ToHeader must be enabled if the SIP provider sends the number of an incoming call in the To field instead of the Request Line field.
This function only affects incoming calls. The configuration can only be changed in WEBconfig or via the command line.
1) Use any web browser to connect to the web interface of the router and navigate to the menu LCOS Menu Tree -> Setup -> Voice-Call-Manager -> Lines -> SIP-Provider -> Line -> <Name of the SIP line>.
Info:
The command-line path is Setup/Voice-Call-Manager/Lines/SIP-Provider/Line/<Name of the SIP line>.
2) Enable or disable the function Trunk-Inc-Cld-In-ToHeader as required.
Using diversion headers:
Diversion headers are used for call diversion. Options for this are as follows:
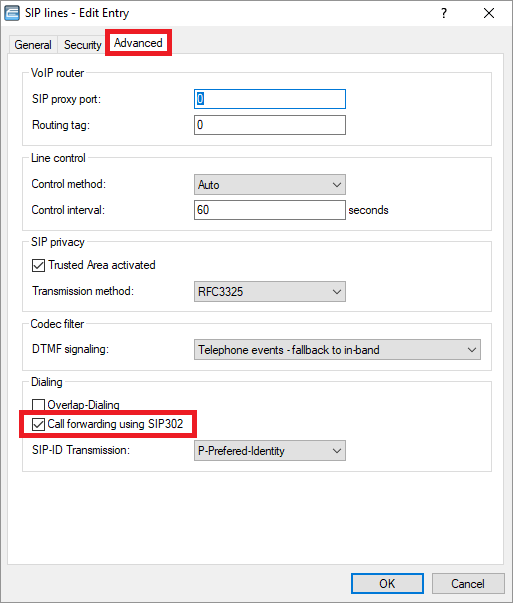
1) SIP 302:
SIP 302 is used to signal call diversion to the provider. That way, no additional voice channel is required to establish a call to the second party.
SIP 302 can only be used with a SIP trunk.
If an ISDN PBX is used, the Partial rerouting / Call deflection feature must be enabled on the PBX.
1.1) Open the configuration for the router in LANconfig and switch to the menu item Voice Call Manager -> Lines -> SIP lines.
1.2 Edit the SIP line, open the Advanced tab, and change the Call forwarding using SIP 302 settings as required.
2) CLIP no screening:
This feature establishes a separate call to the diversion destination, which occupies a second voice channel. At the destination, the number of the diverting line is displayed, not the original number.
CLIP no screening must be supported by the provider. Single accounts are usually not supported.
3) Call transfer at the provider
As with SIP 302, no separate voice channel is required. Call transfer takes place at the provider.
Call transfer at the provider usually only works with single accounts.
Transmission of number fields in outgoing calls (FROM, PPI, PAI):
The SIP ID can be transmitted either in the FROM field, via the P-Preferred Identity (PPI), or via the P-Asserted Identity (PAI).
Depending on the provider, it may be necessary to transmit the SIP ID via a different field, as otherwise the call might be rejected by the provider.
The transmission of the SIP ID is handled differently, depending on whether a SIP trunk or a single account is used.
1) SIP trunk:
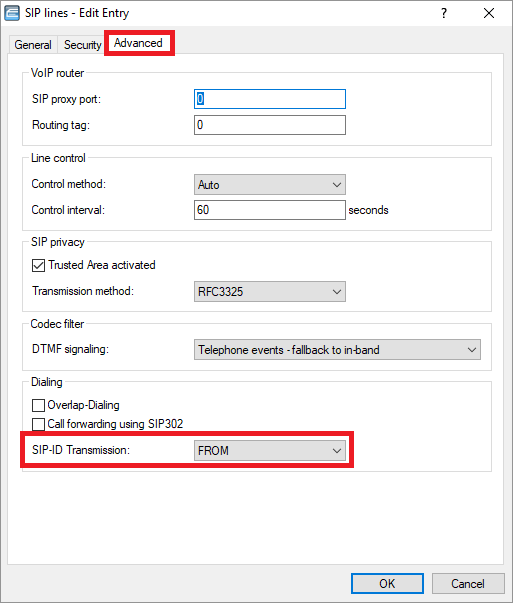
By default, the SIP ID is transmitted via the PPI / PAI. The actual telephone number is transmitted via the FROM field. If required, the configuration can be changed so that the SIP ID is transmitted via the FROM field and the actual number via the PPI / PAI.
1.1) Navigate to the menu Voice Call Manager -> Lines-> SIP lines.
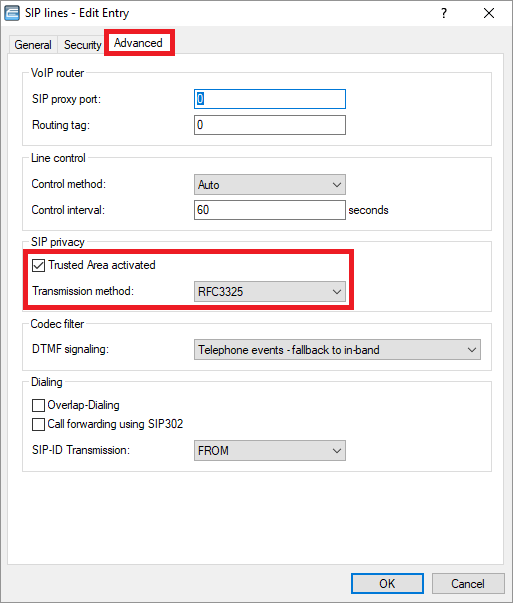
1.2) Edit the SIP line, open the Advanced tab, and select FROM from the drop-down menu for SIP-ID Transmission.
1.3) If the option Trusted Area activated is checked and RFC3325 is selected from the drop-down menu for Transmission method, the PPI is turned into the PAI if the provider is considered a “trusted area”.
Note:
With the setting None, the SIP ID is not transmitted at all, and with the setting IETF-Draft-Sip-Privacy-04, the SIP ID is transmitted as Remote Party ID (RPID).
2) Single account:
The SIP ID is always transmitted in the FROM field.
Transmission of number fields in incoming calls (PPI/ PAI):
In LCOS versions up to 10.30 RU1, only the source telephone number of the SIP client or SIP PBX in the contact header is processed.
With LCOS 10.32 Rel or later, the PPI / PAI is evaluated in addition to the contact header.