
Description:
Wi-Fi clients frequently connect to an access point on a heavily used frequency band, even though an alternative frequency band with free capacities is available. Access points with LCOS LX offer Client Management, which specifically steers Wi-Fi end devices to a different frequency band.
The following steering mechanisms are used:
- Upgrade : The access point steers a Wi-Fi client from the 2.4-GHz band to the 5-GHz band if the signal strength in the 5-GHz band is good enough to improve performance for the Wi-Fi client. This also relieves the 2.4-GHz band.
- Downgrade : The access point steers a Wi-Fi client from the 5-GHz band to the 2.4-GHz band if the signal strength in the 5-GHz band is too weak and the poor data rates consume too much airtime.
- Offloading : The access point steers Wi-Fi clients from the 2.4- to the 5-GHz band or vice versa to relieve a congested frequency band.
Client Management can use the various steering mechanisms both for inactive Wi-Fi clients (idle post-association steering) as well as for active Wi-Fi clients (active post-association steering).
Active Wi-Fi clients can only be steered by 802.11v BTM request (BSS Transition Management) to ensure that their connection is not compromised. With inactive Wi-Fi devices, the preference is to try to use the 802.11v BTM request. If the Wi-Fi client does not support 802.11v BTM or does not respond to the request, the device is disconnected from the Wi-Fi and will be blocked from the frequency band by being entered into a blacklist.
Furthermore, Client Management can ignore probe requests sent by Wi-Fi clients that were previously connected to the access point (pre-association steering). This encourages the devices to connect to the SSID on a different frequency band.
This article describes how to set up Client Management on an access point with LCOS LX.
Requirements:
Procedure:
Open the configuration of the access point in LANconfig and switch to the menu item Wireless-LAN → Client-Management.
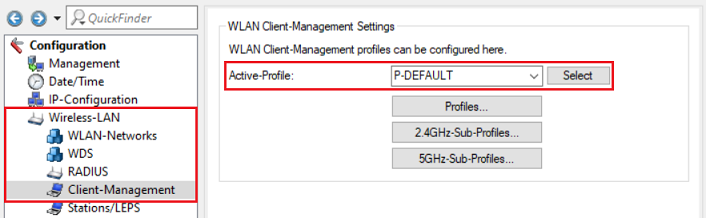
The following three Active Profiles are available:
- P-DEFAULT (default setting):
This profile contains useful default values for most steering mechanisms and is thus the recommended profile. Steering is based on the channel load and the interference detected on the current channel (preferably performed via 802.11v BTM). A Wi-Fi client that does not support 802.11v BTM or does not answer the requests is intentionally disconnected and thus steered to another frequency.
The following steering mechanisms are used/not used in this profile: - Upgrade and Offloading for active and inactive Wi-Fi devices (post-association steering).
- Offloading of Wi-Fi clients by withholding probe responses when frequency bands are congested (pre-association steering).
- However, Offloading of Wi-Fi clients by withholding probe responses (pre-association steering) is not used when frequency bands are not congested, as an Upgrade from the 2.4- to the 5-GHz band could be used instead.
- Downgrade is not used, since most Wi-Fi clients automatically change to the 2.4-GHz band when the signal strength on the 5-GHz band is too weak.
- P-DISABLED:
With this profile, there is no steering. The Wi-Fi client decides for itself which frequency band to use.
- P-LEGACY:
This profile only supports the Upgrade of active Wi-Fi clients from the 2.4- to the 5-GHz band by withholding the probe responses (pre-association steering). In contrast to the P-DEFAULT profile, probe responses are also withheld in the 2.4-GHz band if this is not congested. Additionally, previously connected Wi-Fi clients are moved from the 2.4- to the 5-GHz band. Consequently, the 5-GHz band is always preferred, regardless of the load. This profile corresponds to the LCOS option AP-based band steering.
Profiles:
In addition to the existing profiles, you can also create your own using the Profiles menu. This is only recommended if you have expert knowledge of Wi-Fi. |
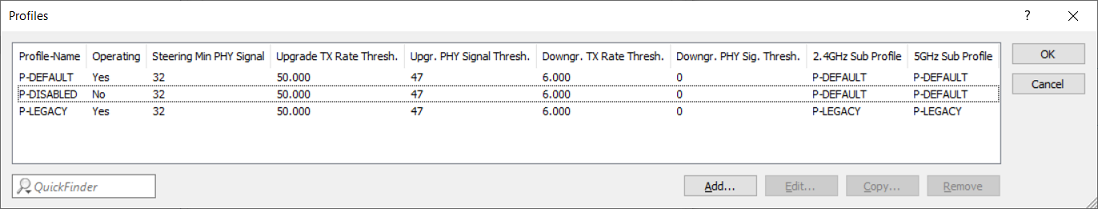
- Profile-Name:
Enter a descriptive name for the profile. - Operating:
Shows whether Client Management is active for this profile. - Steering Min PHY-Signal:
Specifies the signal strength (in dB) from which client steering is initiated (Offloading only). - Upgrade TX Rate Thresh.:
Specifies the limit value of the downlink transmission rate (in kbps), at which the Wi-Fi client should potentially be steered to the 5‑GHz band. In order for steering to be initiated, the Upgr. PHY Signal Thresh. must be reached. - Upgr. PHY Signal Thresh.:
Specifies the minimum uplink signal strength (in dB) required before the Wi-Fi client is steered to the 5‑GHz band. In order for steering to be initiated, the Upgrade TX Rate Thresh. must be reached - Downgrade TX Rate Thresh.:
Specifies the limit value of the downlink transmission rate (in kbps), at which the Wi-Fi client should potentially be steered to the 2.4‑GHz band. - Downgrade PHY Sig. Thresh.:
Specifies the uplink signal strength (in dB) below which the Wi-Fi client is steered to the 2.4‑GHz band. For steering to 2.4 GHz (downgrade), the signal strength has to fall below the value configured here and also the Downgrade TX Rate Thresh. must be reached. - 4GHz Sub Profile:
Select a 2.4GHz Sub Profile. - 5GHz Sub Profile:
Select a 5GHz Sub Profile.
2,4GHz-Sub-Profiles:
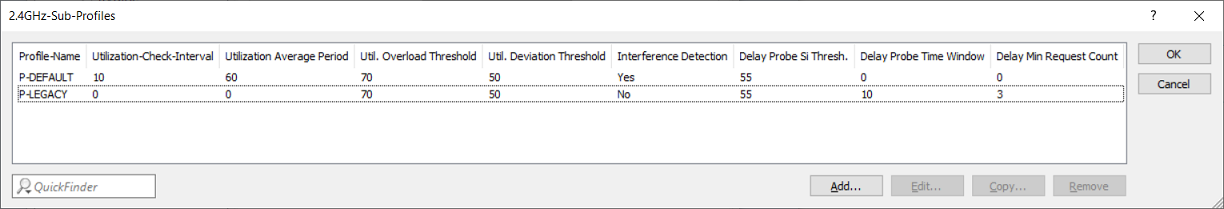
- Profile-Name:
Enter a descriptive name for the profile. - Utilization-Check-Interval:
Configures the interval (in seconds) between channel utilization checks. - Utilization Average Period:
Configures the period (in seconds) used to calculate the average channel utilization. This value must always be higher than the value configured for the Utilization-Check-Interval. - Util. Overload Threshold:
Configures the channel utilization (in percent) above which the current 2.4‑GHz channel is considered to be overloaded. - Util. Deviation Threshold:
Configures the maximum permissible channel utilization (in percent) to be expected after client steering. Once this value is exceeded, any further steering (including Offloading) is prevented (until the next time channel utilization is measured). - Interference Detection:
Configures whether interference on the configured 2.4‑GHz channel is considered for steering. - Delay Probe Si Thresh.:
Specifies the minimum required uplink signal strength (in dB) before upgrade-steering related probe responses to the Wi-Fi client are withheld (does not affect Offloading). - Delay Probe Time Window:
Configures the time window (in seconds) for the purpose of Upgrade steering in which the number of probe requests configured under Delay Min Request Count must be received from the Wi-Fi client in order for these requests to be answered (does not affect Offloading). - Delay Min Request Count:
Configures the number of probe requests for the purpose of Upgrade steering that must be received from a Wi-Fi client within the time configured under Delay Probe Time Window in order for these requests to be answered (does not affect Offloading).
5GHz-Sub-Profiles:
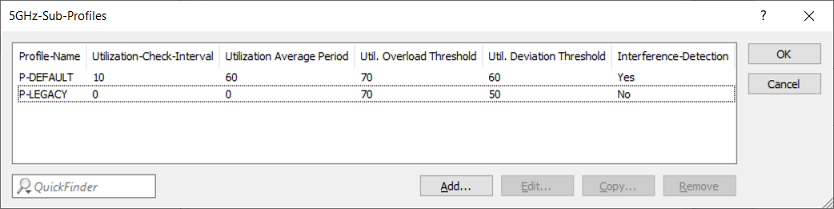
- Profile Name:
Enter a descriptive name for the profile. - Utilization-Check-Interval:
Configures the interval (in seconds) between channel utilization checks. - Utilization Average Period:
Configures the period (in seconds) used to calculate the average channel utilization. This value must always be higher than the value configured for the Utilization-Check-Interval. - Util. Overload Threshold:
Configures the channel utilization (in percent) above which the current 5‑GHz channel is considered to be overloaded. - Util. Deviation Threshold:
Configures the maximum permissible channel utilization (in percent) to be expected after client steering. Once this value is exceeded, any further steering (including Offloading) is prevented (until the next time channel utilization is measured). - Interference-Detection:
Configures whether interference on the configured 5‑GHz channel is considered for steering.



