Description:
In many scenarios a redundant connection of network devices is required, which can only be implemented by redundant cabling. In order to prevent a loop, which would cripple the whole network, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was created. By using STP only the shortest path is set active and the communication is transmitted via this path. When an outage of the active path occurs, a change to another path takes place.
This article describes how Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) can be configured on a switch with LCOS SX 5.xx.
In contrast to STP topology changes happen much faster with RSTP, thus minimizing downtimes.
Requirements:
- One of the following LANCOM switch models:
- XS-51xx / XS-6128QF
- GS-45xx / XS-45xx
- CS-8132F
- YS-7154CF
- LCOS SX as of version 5.10 for XS-51xx / XS-6128QF (download latest version)
- LCOS SX as of version 5.20 for GS-45xx / XS-45xx (download latest version)
- LCOS SX as of version 5.30 for CS-8132F and YS-7154CF (download latest version)
- At least one other network device with active RSTP besides the XS or GS-45xx series switch
Procedure:
1) Configuring RSTP:
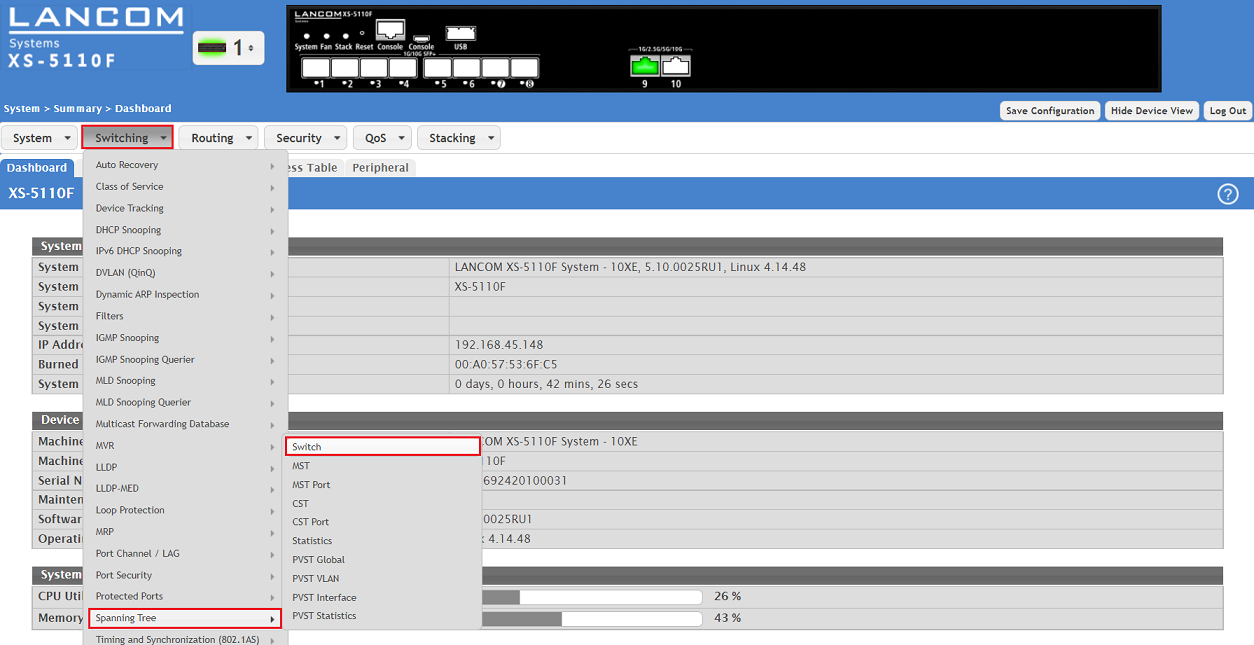
1.1) Connect to the webinterface of the device and go to the menu Switching → Spanning Tree → Switch.
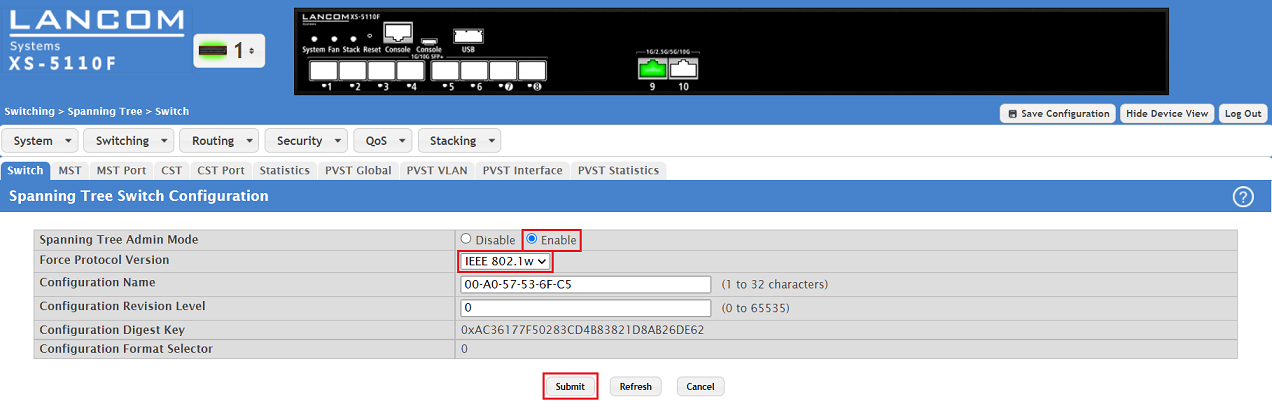
1.2) Modify the following parameters and click Submit:
- Spanning Tree Admin Mode: Make sure, that the option Enable is set.
- Force Protocol Version: In the dropdown menu select the option IEEE 802.1w. This is the designator for RSTP.
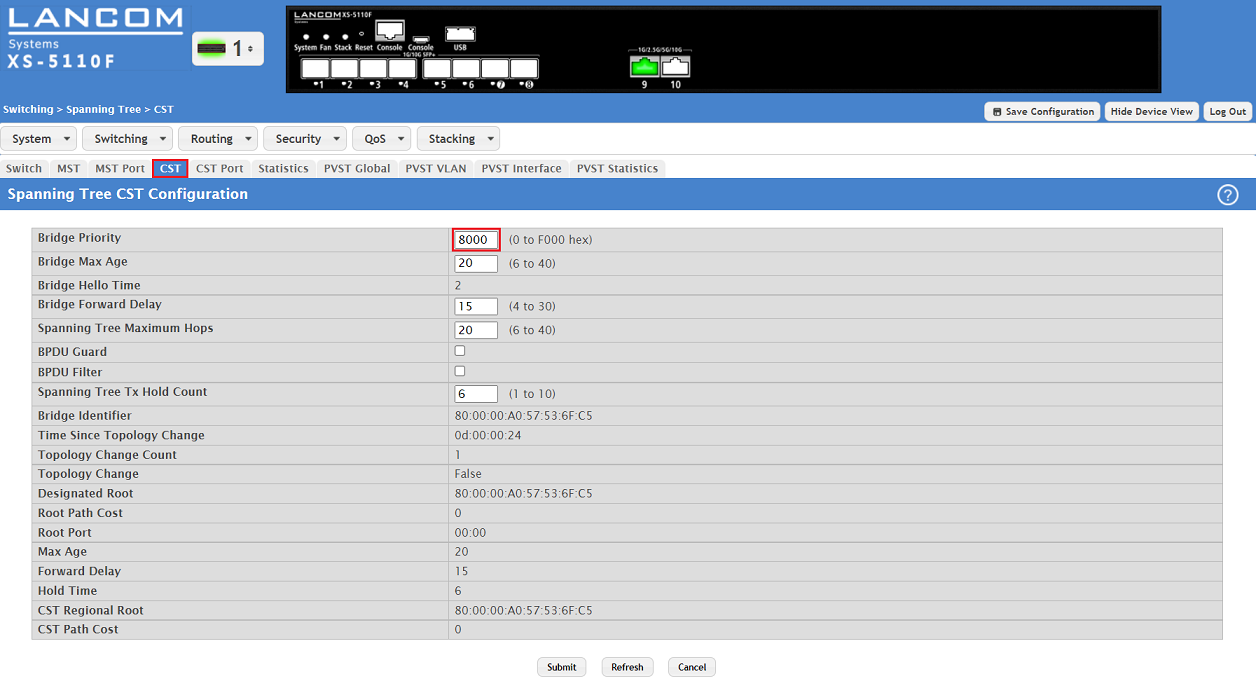
1.3) Go to the tab CST and optionally modify the Bridge Priority.
The lower the value for the Bridge Priority, the higher the priority. The device with the lowest Bridge Priority becomes the Root-Bridge. If two devices have the same Bridge Priority, the device with the lower MAC address becomes the Root-Bridge.
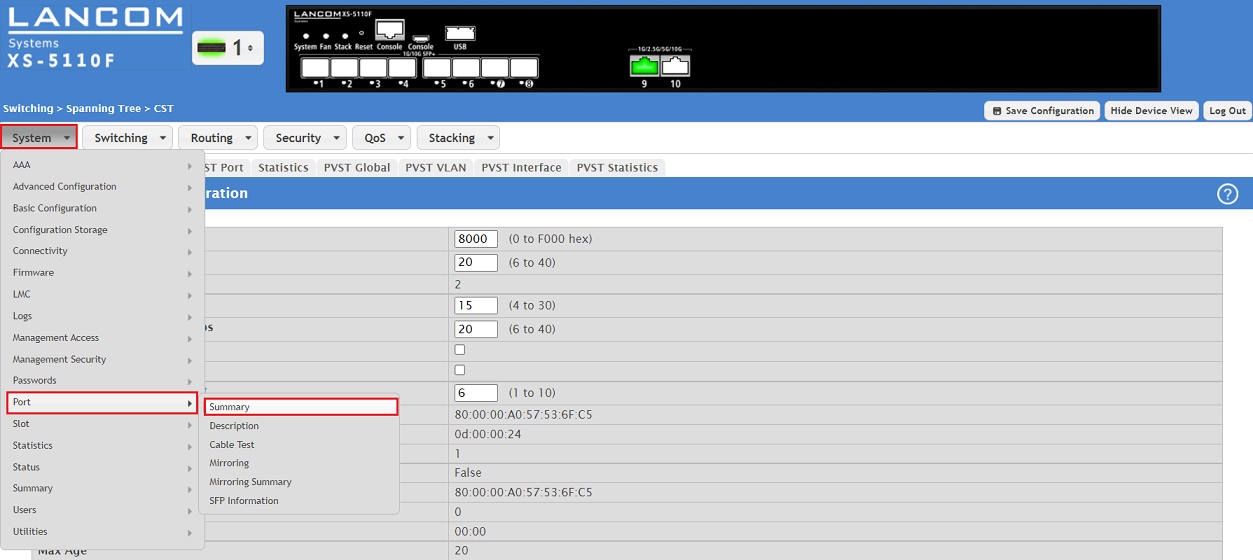
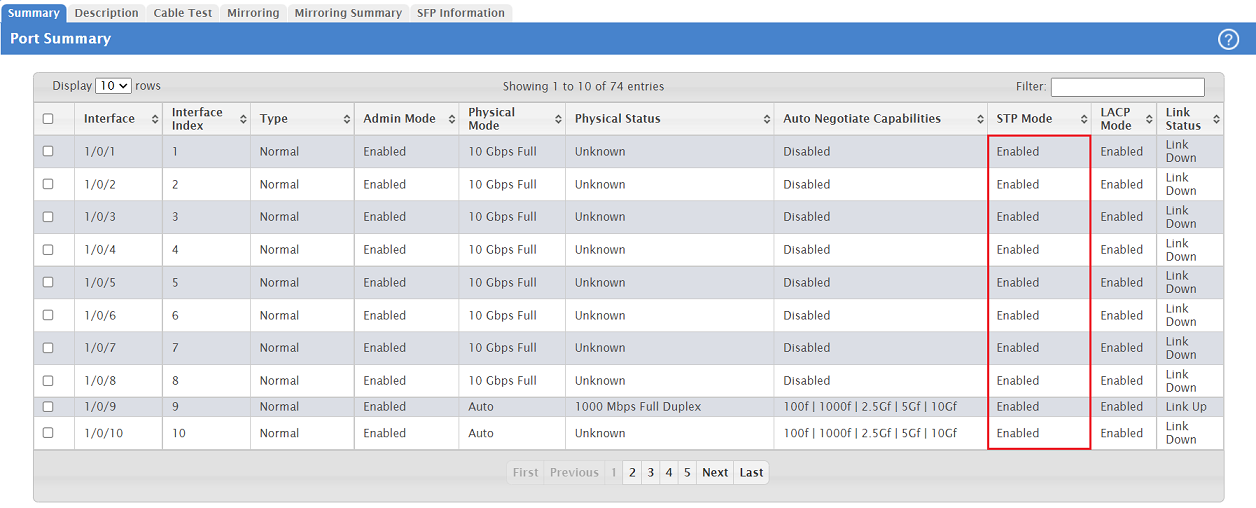
1.4) Go to the menu System → Port → Summary.
1.5) Make sure, that the STP Mode is set to Enabled for all ports (default setting), where RSTP is to be used.
1.6) Click on Save Configuration in the top right-hand corner to save the configuration as the start configuration.
The start configuration is retained even if the device is restarted or there is a power failure.
As an alternative you can also save the configuration as start configuration via the CLI with the command write memory.
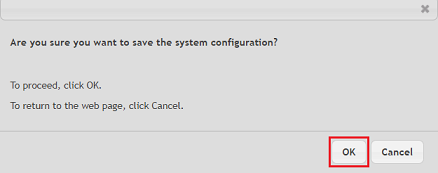
1.7) Acknowledge the save process by clicking OK.
2) Controlling the Spanning Tree status for individual switch ports:
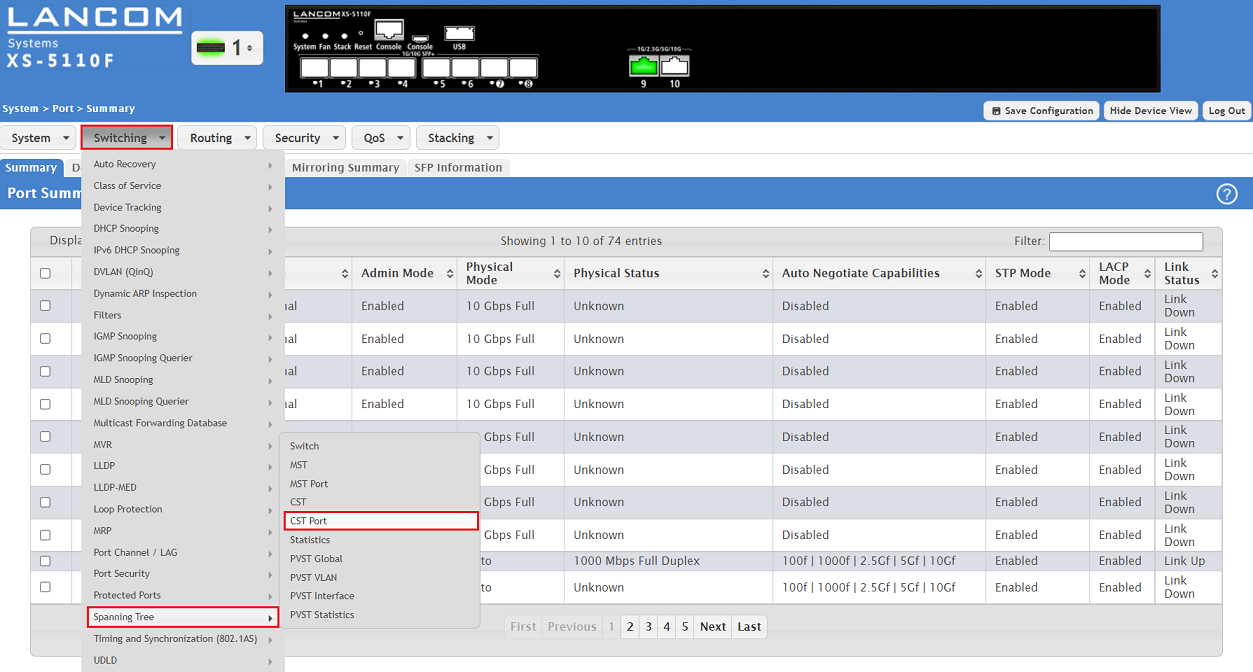
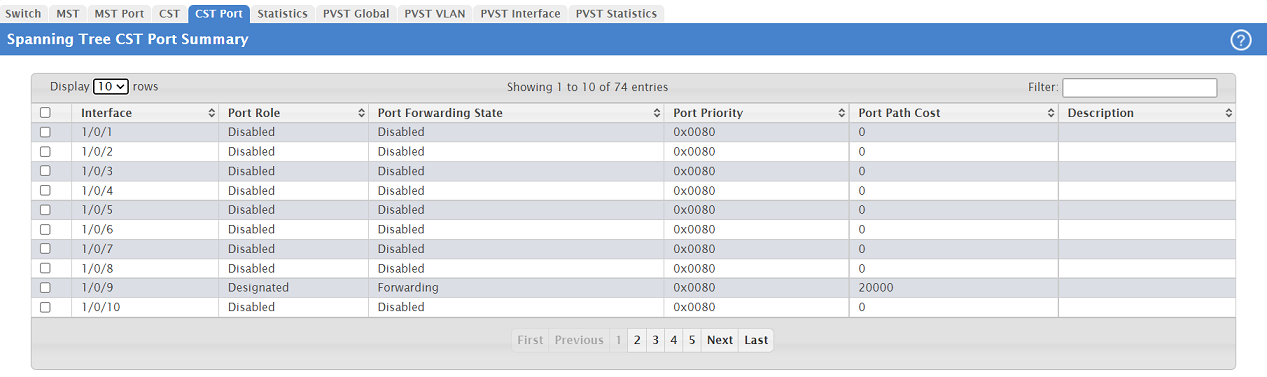
2.1) Go to the menu Switching → Spanning Tree → CST Port.
2.2) The status information for individual switch ports can viewed in the table Spanning Tree CST Port Summary.