Description:
This document describes the configuration steps required on a LANCOM managed switch of the GS-23xx series in order to configure a Voice VLAN. If an LLDP-MED compatible VoIP telephone is connected to the switch, the switch recognizes the telephone and activates the Voice VLAN on the switch port. As the Voice VLAN is tagged on this port (tagging mode
Hybrid), tagging has to be also activated on the VoIP telephone. It is also possible to connect additional network devices to this port, which are to communicate in another VLAN. For this purpose there is a separate port on many VoIP telephones a PC can be connected to for example. This can save an additional switch.
Requirements:
- LANCOM switch of the GS-23xx series with LCOS SX as of 3.32 Rel (download latest version)
- IP telephone supporting LLDP-MED
- Any web browser for accessing the webinterface
- The VoIP telephone has to be configured to tag packets with the Voice VLAN ID (active tagging)
Scenario: - In this example, the Voice VLAN has the ID 200, and LLDP is to be used as the discovery protocol.
- The IP telephone should be assigned this VLAN ID automatically as soon as it is connected to the designated switch port.
 Image showing the configuration settings for a LANCOM VoIP Router and a LANCOM SwitchGSxx, including options for WAN connection and SIP phone.
Image showing the configuration settings for a LANCOM VoIP Router and a LANCOM SwitchGSxx, including options for WAN connection and SIP phone.
Procedure:
1) Connect to the switch via the webinterface, go to the menu Configuration → VLAN → VLAN Membership and click Add New VLAN.
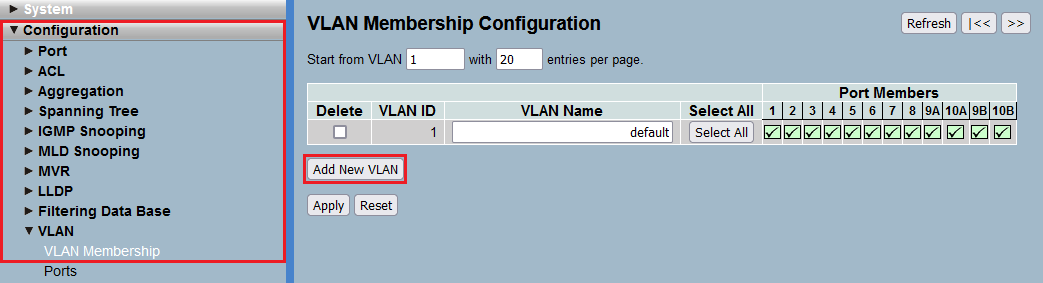 A screenshot of a network configuration interface displaying options for VLAN membership, port aggregation, IGMP and MLD snooping settings, and a filtering database.
A screenshot of a network configuration interface displaying options for VLAN membership, port aggregation, IGMP and MLD snooping settings, and a filtering database.2) Modify the following parameters and click Apply:
- VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID of the Voice VLAN (in this example the VLAN ID 200).
- VLAN Name: Enter a descriptive name for the Voice VLAN (in this example Voice).
- Port Members: Select the Port, the router is connected to (in this example Port 8).
 Screenshot of a VLAN membership configuration interface showing options to add, delete, refresh, and apply settings for VLANs with a list of port members.
Screenshot of a VLAN membership configuration interface showing options to add, delete, refresh, and apply settings for VLANs with a list of port members.
3) Connect the IP telephone to the switch. For this example we use switch port 1.
4) Go to the menu
Configuration → LLDP → LLDP Configuration and set the
Mode to
Enabled for the ports, where a VoIP telephone is connected, to activate LLDP (in this example
Port 1). Click
Apply afterwards.
 A screenshot of a network device's configuration interface displaying settings for LLDP, ACL, Spanning Tree, Port Modes, VLANs, and various disabled features such as Port Statistics and GARP.
A screenshot of a network device's configuration interface displaying settings for LLDP, ACL, Spanning Tree, Port Modes, VLANs, and various disabled features such as Port Statistics and GARP.5) Switch to the menu Configuration → LLDP → LLDP-MED-Configuration.
 A screenshot of a network device configuration menu displaying options such as Port, ACL, Aggregation, Spanning Tree, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, MVR, YLLDP, LLDP Configuration, LLDP Neighbours, LLDP MED Neighbours, and EEE.
A screenshot of a network device configuration menu displaying options such as Port, ACL, Aggregation, Spanning Tree, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, MVR, YLLDP, LLDP Configuration, LLDP Neighbours, LLDP MED Neighbours, and EEE.
6) Under Policies click on the button Add new policy.
 Screenshot of a user interface displaying options to add a new policy, configure policy ports, and buttons to apply or reset changes.
Screenshot of a user interface displaying options to add a new policy, configure policy ports, and buttons to apply or reset changes.
7) For the Policy modify the following parameters and click Apply:
- Application Type: In the dropdown menu select the option Voice.
- Tag: In the dropdown menu select the option Tagged.
- VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID of the Voice VLAN (in this example the VLAN ID 200).
- L2 Priority: Enter the value 6.
- DSCP: Enter the value 49.
 Image depicting a user interface for policy management, showing options to delete, add, and configure policies.
Image depicting a user interface for policy management, showing options to delete, add, and configure policies.
8) In the Policy Port Configuration select the Policy created in step 7) for the Port, the VoIP telephone is connected to (in this example Port 1). Click Apply afterwards.
 Screenshot of a PolicyPortConfiguration menu displaying options including PolicyID and a reset button.
Screenshot of a PolicyPortConfiguration menu displaying options including PolicyID and a reset button.
9) Recheck the LLDP-MED Neighbor information after the LLDP negotiation between the switch and the IP telephone.
 A detailed view of a technical configuration interface displaying various network settings including Spanning Tree, LLDP MED Neighbour Information, IGMP Snooping, MVR device capabilities, and Power over Ethernet options.
A detailed view of a technical configuration interface displaying various network settings including Spanning Tree, LLDP MED Neighbour Information, IGMP Snooping, MVR device capabilities, and Power over Ethernet options.10) Go to the menu Configuration → Voice VLAN → Configuration.
 Screenshot showing a network device configuration menu with various settings including System, Port, ACL, Aggregation, Spanning Tree, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, MVR, LLDP, Filtering DataBase, VLAN, Voice VLAN, and OUI options.
Screenshot showing a network device configuration menu with various settings including System, Port, ACL, Aggregation, Spanning Tree, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, MVR, LLDP, Filtering DataBase, VLAN, Voice VLAN, and OUI options. 11) Under Voice VLAN Configuration mify the following parameters:
- Mode: In the dropdown menu select the option Enabled to activate the Voice VLAN.
- VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID of the Voice VLAN (in this example the VLAN ID 200).
 A screenshot showing a configuration menu for Voice VLAN with options to enable mode, set VLAN ID, adjust aging time in seconds, and select high traffic class.
A screenshot showing a configuration menu for Voice VLAN with options to enable mode, set VLAN ID, adjust aging time in seconds, and select high traffic class.
12) Under Port Configuration modify the following parameters for the Port, the VoIP telephone is connected to. Click Apply afterwards.
- Mode: In the dropdown menu select the option Auto.
- Discovery Protocol: In the dropdown menu select the option LLDP.
 Image showing a configuration menu for port settings with multiple options listed as 'Disabled' under categories like Port Mode, Security, and Discovery Protocol.
Image showing a configuration menu for port settings with multiple options listed as 'Disabled' under categories like Port Mode, Security, and Discovery Protocol.
13) Go to the menu
Configuration → VLAN → Switch Status and make sure that
Port 1 is a member of the VLAN with the ID 200.
 Image of a network configuration interface displaying options such as VLAN Membership Status, Spanning Tree Protocol settings, and other various fragmented technical terms.
Image of a network configuration interface displaying options such as VLAN Membership Status, Spanning Tree Protocol settings, and other various fragmented technical terms.
14) Navigate to the menu Maintenance → Save/Restore → Save Start und save the configuration as Start Configuration.
 Screenshot of a system configuration menu with options to save start configuration, restart device, manage firmware, and reset to factory defaults.
Screenshot of a system configuration menu with options to save start configuration, restart device, manage firmware, and reset to factory defaults.
To check the functionality
please connect a PC to the switch, e.g. to port 3 and perform the following configuration on the switch:
- Port 3 must be a member of the VLAN with the ID 200.
 The image displays a complex user interface for network configuration including options like Spanning Tree, VLAN Membership Configuration, LLDP Configuration, and Delete VLAN ID among other settings.
The image displays a complex user interface for network configuration including options like Spanning Tree, VLAN Membership Configuration, LLDP Configuration, and Delete VLAN ID among other settings. - In the VLAN port configuration, port 3 needs to be set with the PVID 200.
 Image of a complex network configuration interface showing various settings such as VLAN port configurations, port types, ingress filtering, frame type, egress rules, PVID settings, and Spanning Tree configurations.
Image of a complex network configuration interface showing various settings such as VLAN port configurations, port types, ingress filtering, frame type, egress rules, PVID settings, and Spanning Tree configurations. - Save the configuration to the switch. You should now be able to send a ping from the PC connected to port 3 to the IP telephone connected to port 1.

















