In certain cases, the LANCOM Management Cloud may be unable to roll out a configuration to the device due to an invalid parameter. In this case an OID error is output to the device log.
There could be an invalid parameter either in the configuration of the device itself or in the LMC configuration.
This article describes how to identify and correct the invalid parameter from the command line or via the LMC.
1) The invalid parameter is in the configuration of the LANCOM Management Cloud:
1.1) Connect to the LMC, click Devices and then click the affected device.
1.2) Click on Detail configuration.
1.3) Enter the OID ID mentioned in the error message in the Quickfinder to open the affected menu (in this case Public Spot → Authentication → Authentication mode). Change the parameter to the desired value afterwards.
Proceed with the analysis and troubleshooting as described in
this Knowledge Base article.
2.1) Connect to the LMC, click Devices and then click the affected device.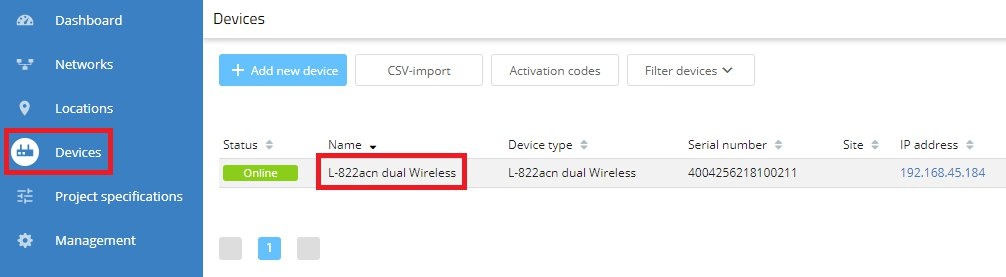
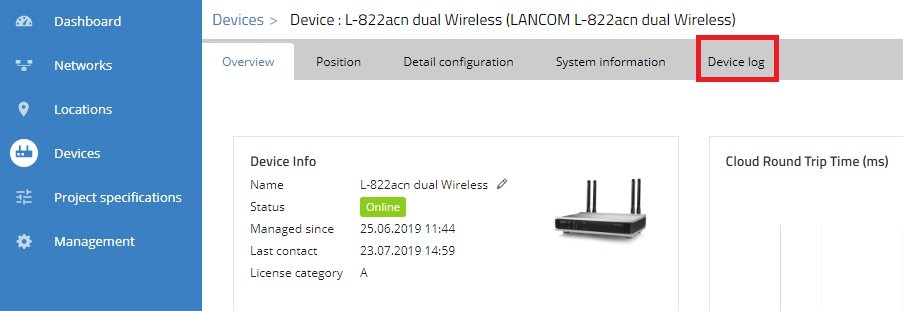
2.2) Click Device log to find the problematic value.
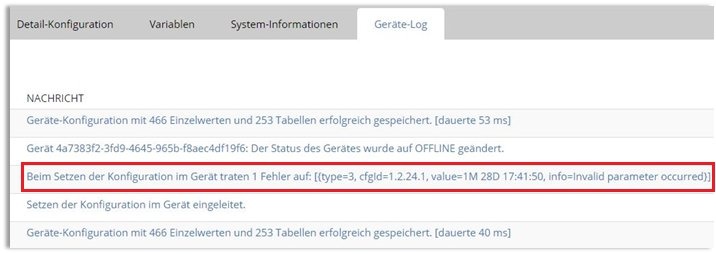
2.3) Make a note of the OID shown as the “cfgid” in the error message, along with the invalid value.
2.4) Download the english Menu Reference Guide to check which command-line path is behind the OID.
2.5) In the Menu Reference Guide, look for the OID while omitting the first and last digits. In this example, this would be 2.24. This points to the console path Setup/Public-Spot-Module. The parameter 1 refers to the authentication mode.
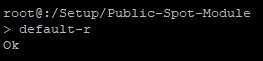
2.6) Reset the table to its default settings with the command default -r.
2.7) Now check whether the configuration can be rolled out via the LMC. If necessary, repeat the above steps for any further invalid parameters.