This document deals with a number of reasons why data transmission may not be possible even if you have successfully established a VPN connection with the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client.
It is impossible to communicate via the VPN tunnel, even though the tunnel has been established. As illustrated in the image below, the VPN connection is established, but we have not received any RX data packets from the remote network.
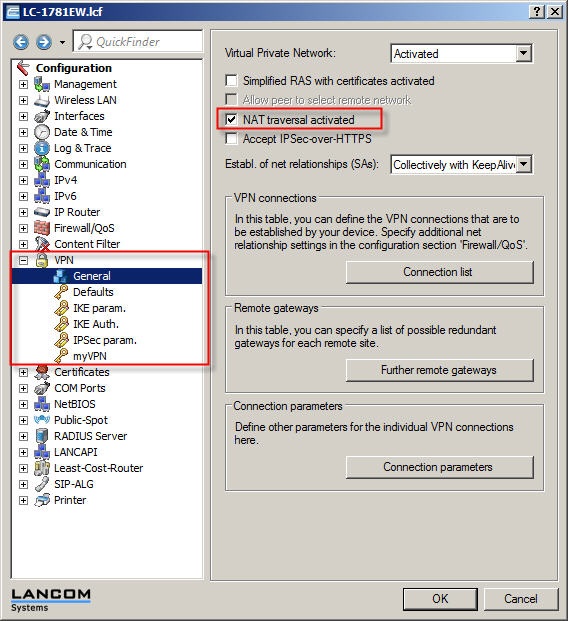
1.1) Check if
NAT-traversal is activated on the remote router you wish to connect to in the menu item
VPN → General.
Step 2:
Check the order or the network adapters as found by your operating system.
Windows Vista, Windows 7 & Windows 8:
2.1) Open the Network and Sharing Center via Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center.
2.2) Click on the option Change adapter settings.
2.3) Open you the menu Advanced → Advanced settings.
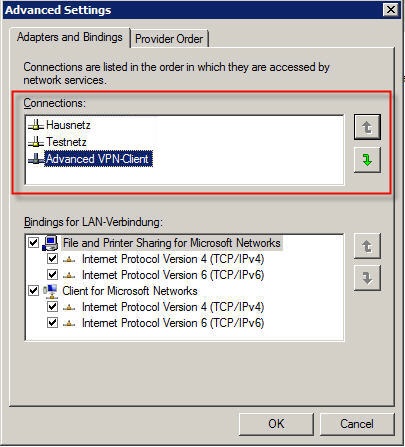
2.4) Re-order your network adapters as follows:
- First position: Physical network adapter
- Middle position: WLAN network adapters, Firewire, UMTS, etc.
- Final position: Virtual network adapter LANCOM Advanced VPN Client
These changes come into effect after the computer's operating system is restarted.
Step 3:
Add the remote local IP network to the VPN configuration of the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client.
3.1) In the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client, open the menu Configuration → Profiles.
3.2) Select the profile which you wish to edit and click on the Edit button.
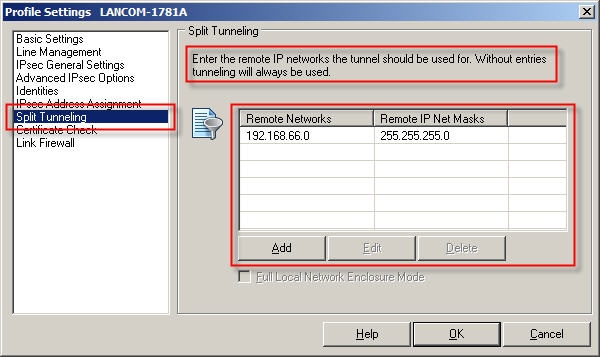
3.3) Navigate to the menu Split tunneling.
3.4) Enter the local IP network(s) which are to be accessed via the VPN tunnel.
If you do not specify an IP network here, your Internet traffic will also be directed via the VPN tunnel!
Step 4:
Check if you require an IPSec pass-through, or whether this has been set up already.
By default an IPSec connection uses the port 500 UDP, the IP protocol ESP (50), or port 4500 UDP. The VPN tunnel may occasionally be directed via routers which do not support IPSec pass-through. In these cases, the IPSec packets may be handled incorrectly, or they may even be dropped.
A result of this is that, even though the tunnel has been established, it cannot be used for communications. This problem can be avoided by activating port forwarding for the UDP ports 500 and 4500 on the client-side of the router.
Step 5:
If you cannot use IPSec pass-through, you have the option of setting up a VPN connection based on IPSec over HTTPS. All you have to do in this case is to open the HTTPS port 443.
With IPSec over HTTPS, an attempt is first made to transfer data using standard IPSec. If the connection cannot be established (e.g. because IKE port 500 is blocked), then an attempt is then automatically made to establish a connection that encapsulates the IPSec VPN in an additional SSL header (port 443, like HTTPS).
For a guide on setting up a VPN with IPSec over HTTPS, see this KnowledgeBase document ( ).
).
Step 6 – other possible error sources:
Generally speaking, the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client is not the only security software installed on a system to protect it from unauthorized access.
The system may also be running a virus scanner, a firewall, and/or a Spy Doctor. These programs often integrate deeply into the system, and they can cause software conflicts. A potential effect of this is that the LANCOM Advanced VPN Client may not be able to communicate over an active VPN tunnel.
In this case the connection problems cannot be solved simply by deactivating the program. To find out whether the programs being used are affecting communications, they must first be uninstalled and the operating system then restarted. LANCOM Systems has experienced problems of this nature with the programs listed below. The only way of assisting our customers was for them to uninstall this anti-virus or firewall software:
- Norton Internet Security
- Panda Antivirus
- Trendmicro
- Kasperski
For
a description of how to set up a VPN client connection via 3G or 4G, see the following KnowledgeBase article (

).
In this example the workstation has just one default gateway.